Hashing based technique for Nearest neighbor search
Nearest neighbor search is a popular phenomenon for finding the most similar data example to a given query. Similar to K-nearest neighbor clustering, we rely on a given distance metric like euclidean, hamming distance or jaccard similarity to determine the similarity structure of the data. Distance metrics are influenced by the kind of data for example makes sense to hamming distance metric for image data. Nearest neighbor search is useful in many applications like image retrieval, document search. The concept enforces search not only for duplicates but also the most similar in terms of content and context. Imagine with the millions of documents on the internet, how does a search engine zero down to only relevant documents/web pages in just milliseconds. A similarity search in such a high dimensional space can be likened to a linear search where by each data example is compared to the query. This is not feasible for such a search space like the internet. However, search can be optimised by the use of hashing - hashing based nearest neighbor search.. Hashing, in broad terms, refers to mapping of data points to a compact code of finite length.
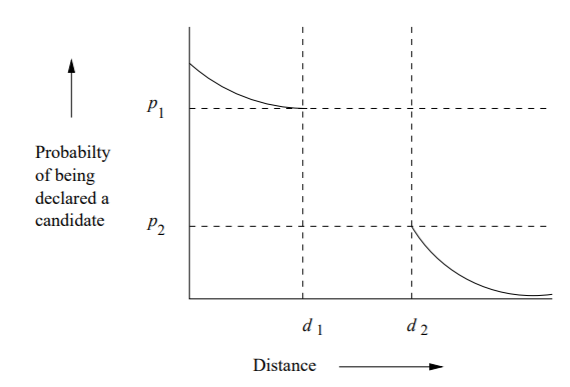
Locality sensitive hashing is a hashing technique that relies on the principle of maximizing of probability of collision for objects that are similar as compared to those that are far apart. This can be referred to as “sensitivity”. In this context, collision refers to mapping multiple hash codes to the same bucket. As opposed to generic hashing that avoids collision, LSH relies on this phenomenon to aid the nearest neighbor search. Sensitivity can be defined as; \(\rho = \frac{log(1/p1)}{log(1/p2)}\)
Where; p1 is the collision probability for nearby points, p2 is the collision probability for points that are far apart and \(\rho\) is the measure of how sensitive the hash function is to distance.
Illustration of sensitivity
The space complexity for the above definition is \(O(dn+n^{1+\rho})\), query time complexity- \(O(n^{\rho})\)
With the ability to quantify sensitivity, this technique can imposed over several hashing functions which store hash codes in buckets/ repositories and in essence on query, similar objects will be placed to the same bucket. This is illustrated in figure below.
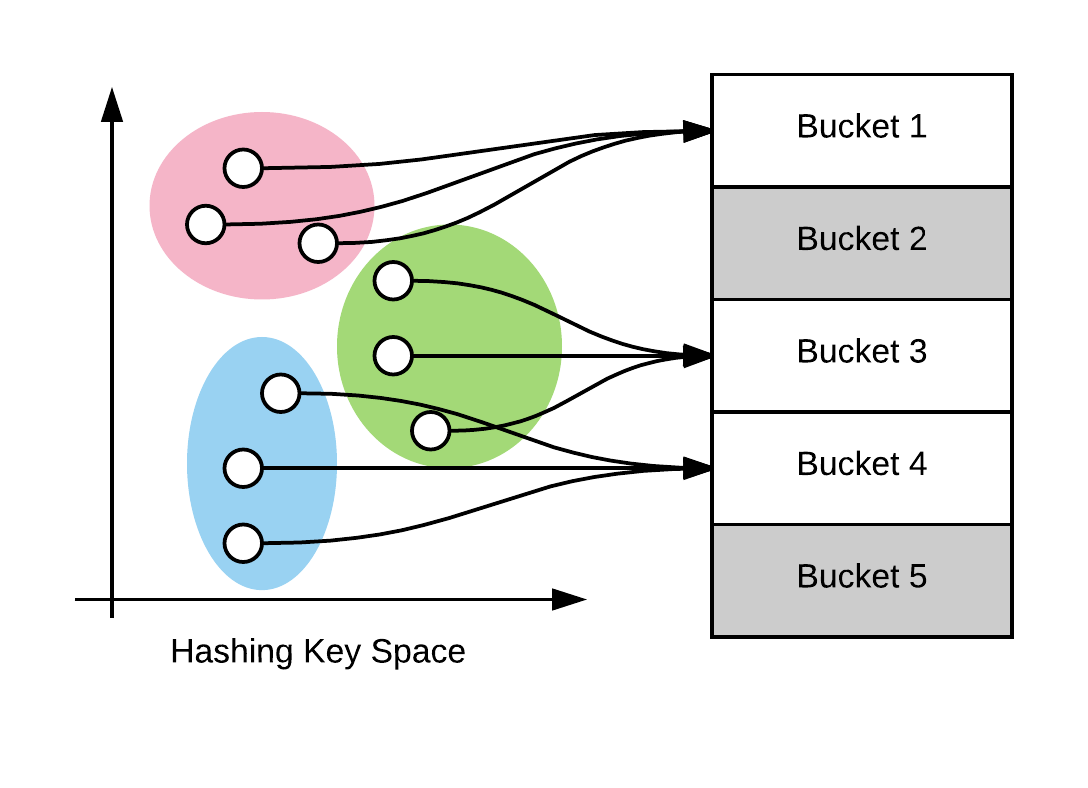
Hashing of similar data points to the same buckets
Therefore, given a query, LSH has the ability to approximate similar data points based on the bucket of the query.There can be constraints to this technique as the hashing is conducted randomly. This also explains the phenomenon of data independence and how the hashing function does not maintain the similarity structure of the input data based on any distance metric. This structure is not represented in the output hash code.
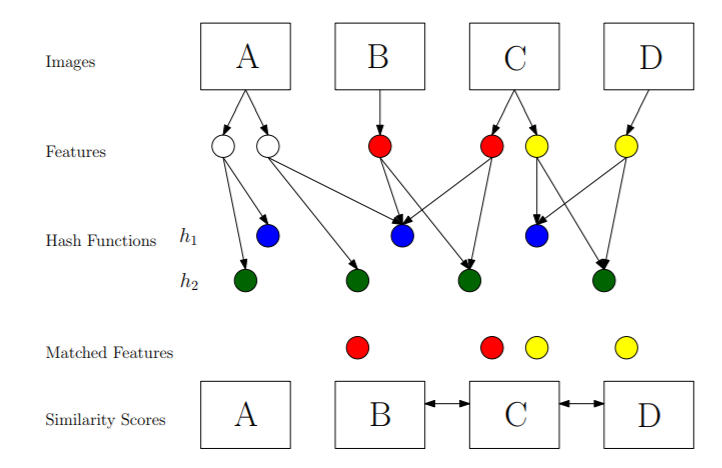
LSH is commonly experimented with document/text search. However, Image search would also be applicable, where similarity is based on the image features. The images are processed with global descriptors such as color histograms and then compared with distance metrics as shown in the figure below. LSH is employed by Google together with other variations to implement the VisualRank algorithm for image search.
Features hashed into the same bin are considered similar when using LSH for image similarity
Drawback of LSH
LSH relies on random hashing or projections of data. Random hashing or projections of data leaves the possibility that similar objects might end up in different buckets and this adversely affects the nearest neighbor search. Despite this being a shortfall, the randomness of LSH gives it a fast query time, a small memory footprint and a fair approximate in relation to the traditional nearest neighbor search. This further introduces the query time and accuracy trade-off which is highly dependant on the scenario or application. Would a user rather wait for accurate results or get an approximate in timely manner?
Other methods that exist are variations of locality preserving hashing which is theoretically more accurate as it’s projections maintain the neighborhood structure of the original data hence the hash codes are structured the same. However, this might not be practical in real world applications as it suffers from more query time and fast query time is an important aspect for the technology climate.
The trade-off is between query time and accuracy. Which one is more important in a given application?
Where is LSH being used?
- Uber- detect fraudulent trips and driving - Explained
- Pinterest- for image similarity - Explained
- Google - Image search with PageRank - Explained