Exploring the possibility to predict financial market prices with regression techniques
Financial time series analysis is a complex and active research field surrounding the ability to accurately predict the future performance of economic trends. A popular example of financial time series is stock market prices showcasing the trends of price fluctuation over a given period of time. Stock prices are influenced by external macroeconomic factors like political and socio-economic occurrences which are often difficult to predict. This makes the financial time series trend semi-stochastic and contributes to the complexity of accurate prediction. The objective of this study is to quantify the econometric relationship between variables that represent the price changes in the past.
A couple of regression models can be explored to predict the future occurrence of such series. I explored some of these models i.e;
- Multivariate linear regression that takes into account the multivariate nature of target variables and interdependence between predictor variables
- Polynomial regression where polynomial functions of the predictor variables are fit to the target values
- Random forest regression that averages output from randomly split regression trees
- Vector autoregressive models where values from a time series are regressed on previous values from that same time series and predictor variables.
Of these methods, vector autoregressive models have been the most successful in previous econometric model research, however, for this particular study, random forest regression exhibited the most stable and consistent predictions as will be discussed in the results section. A comparative study of these models is conducted on multiple stocks and analysis based on the R squared values of individual models. From the results, bagging regression trees into a random forest produces consistent results which are instrumental for prediction of time series data
This blog is an extraction of research I conducted on proprietary data of a multivariate nature with this specific topic and for illustration purposes, two of the outstanding methods that exhibited considerably usable results;
Random forest regression
A set of binary decision trees derived from data observations sampled independently and a subset of predictor variables selected at random are combined to form a random forest. Upon fitting of the samples onto the ensemble or collection of decision trees, the output of the regression is obtained by averaging the values from the individual and approximately unbiased regression trees. This can also be referred to as bagging, which improves accuracy, stability and also prevents overfitting of the random forest.
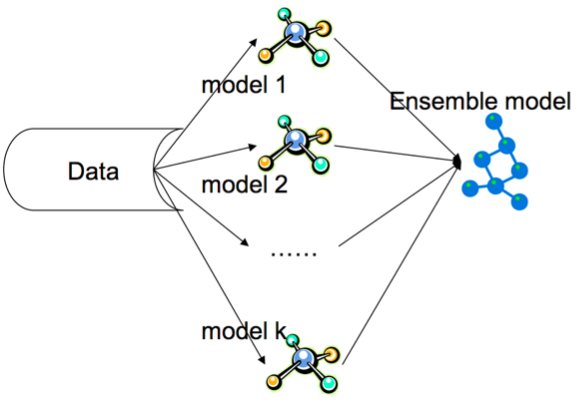
Random Forest regression. Image from Acadglid
Vector autoregressive(VAR) Models
An autoregressive model is when a value from a time series is regressed on previous values from that same time series \(y_t = \beta_0 + \beta_1 y_{t-1} + \epsilon_t\)
For a given time \(t\), the value, \(y_t\) is dependent on the previous time period \(y_{t-1}\). The order of an auto-regression is the number of immediately preceding values used to predict the current value.This is also referred to as the lag of the auto-regression. For \(k^{th}\) order autoregression, the values of the series at any time t is a linear function of the values at time \(t-1 \cdots t-k\).
Definition of the VAR model:
Given a time series vector of variables, $n \times 1$, defined as \(Y_t = (y_{1t}, y_{1t}, \cdot, y_{nt}\). A vector autoregressive of lag p is defined as; \(Y_t = c + \Pi_1 Y_{t-1} + \Pi_2 Y_{t-2} + \dots + \Pi_p Y_{t-p} + \epsilon_t, t = 1, \dots, T\)
where \(\Pi\) is the coefficient matrix at a given time \(t\)
Vector autoregressive models are popular with financial econometrics research because of how flexible the predictions from the VAR models are i.e they can be conditionally determined by the potential values of the specified variables in the model.However VAR models are constrained by the structure of data.
Efficient Market Hypothesis
Some argue that financial time series prediction is not possible. The best prediction is only the current price of the stock; which is the efficient market hypothesis. This because financial markets are influenced by external unquantifiable factors like political affairs. This adds complexity to this task.
Resources
- Vector Autoregressive for Multivariate Time Series by E.Zivot and J.Wang, 2006
- The Elements of Statistical Learning by T.H.R.J. Friedman, 2009
- Efficient Markets Theory: Historical Perspectives by F.Jovanovic, 2010
